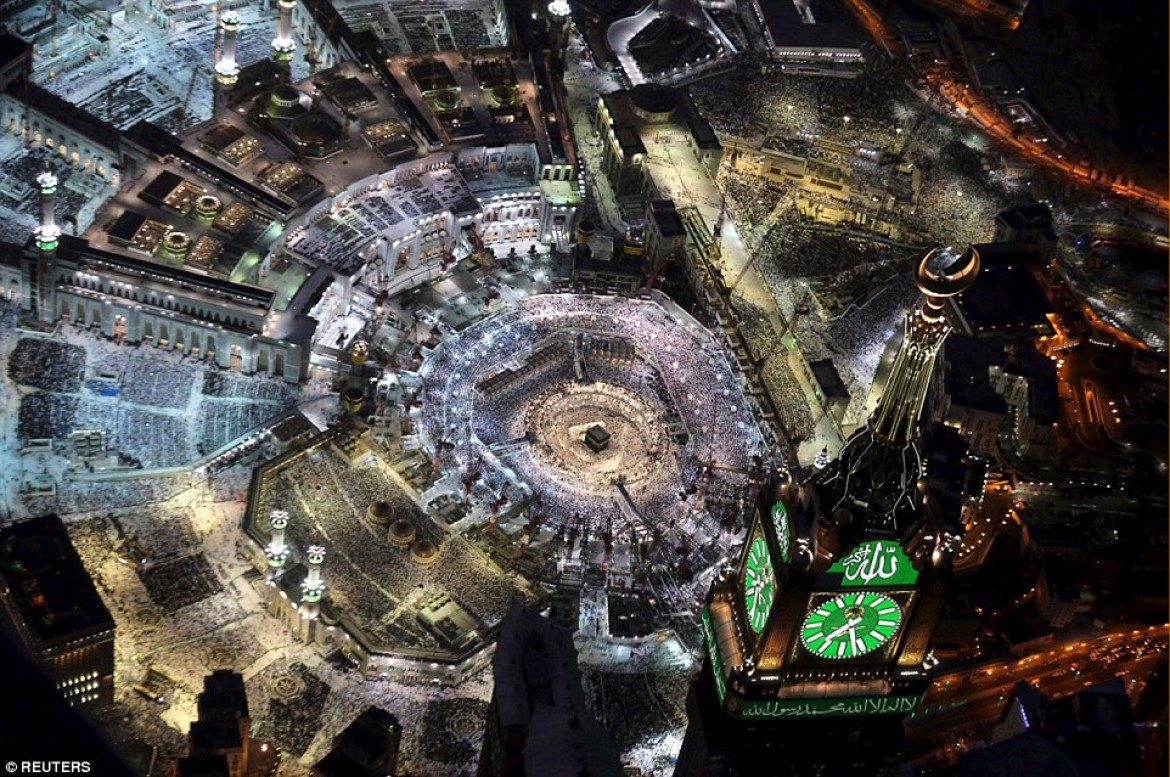
About Masjid Al-Haram
Masjid al-Haram (Inviolable Mosque), also known as the Great Mosque of Mecca, is a mosque that surrounds the Kaaba in Mecca, in the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia. It is a site of pilgrimage in the Hajj, which every Muslim must do at least once in their lives if able, and is also the main phase for the ʿUmrah, the lesser pilgrimage that can be undertaken any time of the year. The rites of both pilgrimages include circumambulating the Kaaba within the mosque. The Great Mosque includes other important significant sites, including the Black Stone, the Zamzam Well, Maqam Ibrahim, and the hills of Safa and Marwa.
As of August 2020, the Great Mosque is the largest mosque and the eighth largest building in the world. It has undergone major renovations and expansions through the years. It has passed through the control of various caliphs, sultans and kings, and is now under the control of the King of Saudi Arabia who is titled the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques.
History
The Great Mosque contends with the Mosque of the Companions in the Eritrean city of Massawa and Quba Mosque in Medina as the oldest mosque. Some scholars, who reference Islamic tradition and the Quran, explain that the Islamic perspective claims that Islam as a religion preceded Muhammad, representing previous prophets such as Abraham. Abraham is credited by Muslims with having built the Kaaba in Mecca, and consequently its sanctuary, which according to the Muslim view is seen as the first mosque that ever existed. According to other scholars, Islam started during the lifetime of Muhammad in the 7th century CE, and so did architectural components such as the mosque. In that case, either the Mosque of the Companions or Quba Mosque would be the first mosque that was built in the history of Islam.
Era of Prophet Abraham PBUH and Prophet Ishmael PBUH
According to Islamic doctrine in the Quran, Prophet Abraham PBUH together with his son Prophet Ishmael PBUH raised the foundations of a house, which has been identified as the Kaaba. God showed Prophet Abraham PBUH the exact site which was previously built by Adam PBUH, very near to what is now the ZAMZAM Well, where Abraham and Ishmael began work on the construction of the Kaaba. After Abraham had built the Kaaba, an angel brought to him the Black Stone, a celestial stone that, according to tradition, had fallen from Heaven on the nearby hill Abu Qubays. The Black Stone is believed by Islamic scholars to be the only remnant of the original structure made by Abraham.
After placing the Black Stone in the Eastern corner of the Kaaba, Abraham received a revelation, in which God told the aged prophet that he should now go and proclaim the pilgrimage to mankind, so that men may come both from Arabia and from lands far away, on camel and on foot.
Era of Prophet Muhammad PBUH
Upon Muhammad's victorious return to Mecca in 630 CE, he broke the idols in and around the Kaaba, similar to what, according to the Quran, Abraham did in his homeland.[citation needed] Thus ended polytheistic use of the Kaaba, and began monotheistic rule over it and its sanctuary.
Umayyad era
The first major renovation to the mosque took place in 692 on the orders of Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. Before this renovation, which included the mosque's outer walls being raised and decoration added to the ceiling, the mosque was a small open area with the Kaaba at the center. By the end of the 8th century, the mosque's old wooden columns had been replaced with marble columns and the wings of the prayer hall had been extended on both sides along with the addition of a minaret on the orders of Al-Walid I. The spread of Islam in the Middle East and the influx of pilgrims required an almost complete rebuilding of the site which included adding more marble and three more minarets.
Ottoman era
In 1570, Sultan Selim II commissioned the chief architect Mimar Sinan to renovate the mosque. This renovation resulted in the replacement of the flat roof with domes decorated with calligraphy internally, and the placement of new support columns which are acknowledged as the earliest architectural features of the present mosque. These features are the oldest surviving parts of the building.
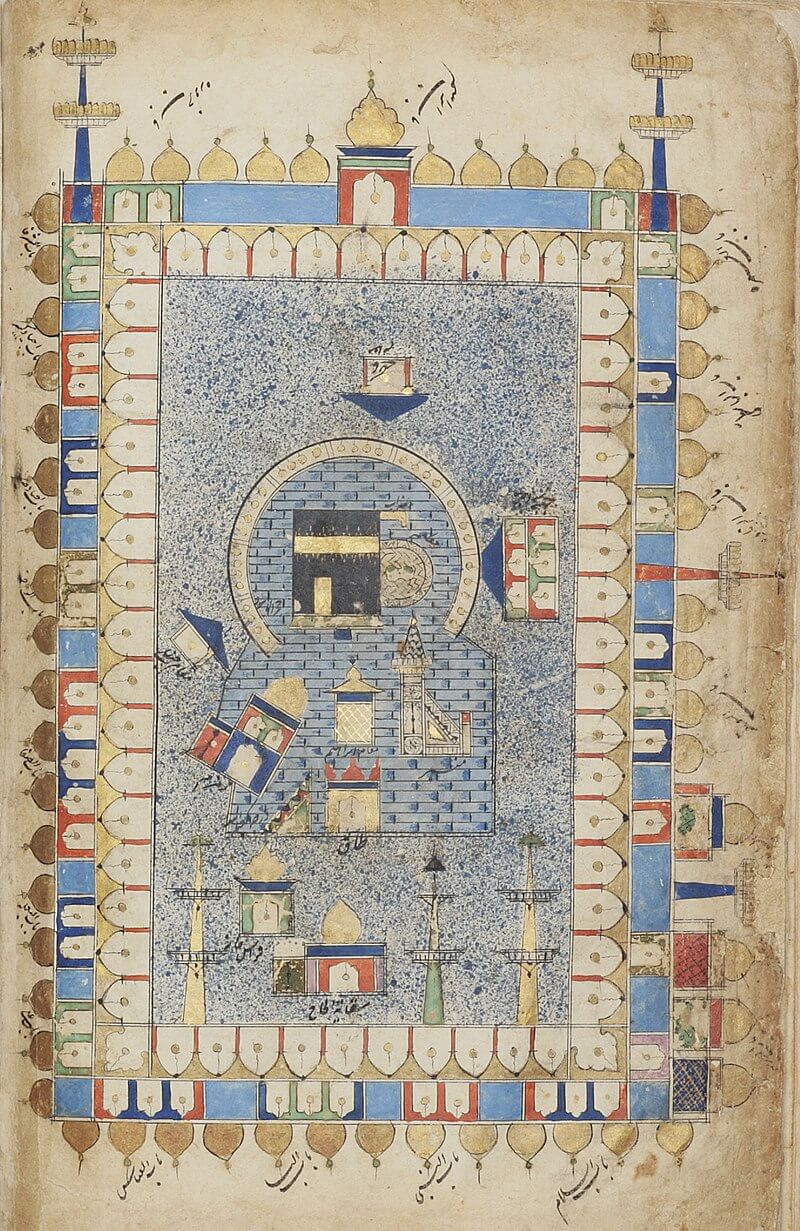 The Great Mosque in an illustration of the Futuh al-Haramayn of Muhi Al-Din Lari, 1582
The Great Mosque in an illustration of the Futuh al-Haramayn of Muhi Al-Din Lari, 1582
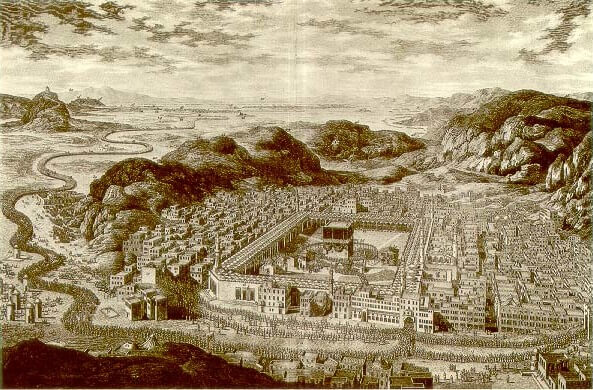 The mosque in 1850, during the Ottoman period
The mosque in 1850, during the Ottoman period
 The mosque in 1910, during the Ottoman period
The mosque in 1910, during the Ottoman period
During heavy rains and flash floods in 1621 and 1629, the walls of the Kaaba and the mosque suffered extensive damage. In 1629, during the reign of Sultan Murad IV, the mosque was renovated. In the renovation of the mosque, a new stone arcade was added, three more minarets (bringing the total to seven) were built, and the marble flooring was retiled. This was the unaltered state of the mosque for nearly three centuries.
Saudi era
First Saudi expansion
The first major renovation under the Saudi kings was done between 1955 and 1973. In this renovation, four more minarets were added, the ceiling was refurnished, and the floor was replaced with artificial stone and marble. The Mas'a gallery (As-Safa and Al-Marwah) is included in the Mosque, via roofing and enclosures. During this renovation many of the historical features built by the Ottomans, particularly the support columns, were demolished.
On 20 November 1979, the Great Mosque was seized by extremist insurgents who called for the overthrow of the Saudi dynasty. They took hostages and in the ensuing siege hundreds were killed. These events came as a shock to the Islamic world, as violence is strictly forbidden within the mosque.
Second Saudi expansion
The second Saudi renovations under King Fahd, added a new wing and an outdoor prayer area to the mosque. The new wing, which is also for prayers, is reached through the King Fahd Gate. This extension was performed between 1982 and 1988.
1988 to 2005 saw the building of more minarets, the erecting of a King's residence overlooking the mosque and more prayer area in and around the mosque itself. These developments took place simultaneously with those in Arafat, Mina and Muzdalifah. This extension also added 18 more gates, three domes corresponding in position to each gate and the installation of nearly 500 marble columns. Other modern developments added heated floors, air conditioning, escalators and a drainage system.
Third Saudi expansion
In 2008, the Saudi government under King Abdullah Ibn Abdulaziz announced an expansion of the mosque, involving the expropriation of land to the north and northwest of the mosque covering 300,000 m2 (3,200,000 sq ft). At that time, the mosque covered an area of 356,800 m2 (3,841,000 sq ft) including indoor and outdoor praying spaces. 40 billion riyals (US$10.6 billion) was allocated for the expansion project.
In August 2011, the government under King Abdullah announced further details of the expansion. It would cover an area of 400,000 m2 (4,300,000 sq ft) and accommodate 1.2 million worshippers, including a multi-level extension on the north side of the complex, new stairways and tunnels, a gate named after King Abdullah, and two minarets, bringing the total number of minarets to eleven. The circumambulation areas (Mataf) around the Kaaba would be expanded and all closed spaces receive air conditioning. After completion, it would raise the mosque's capacity from 770,000 to over 2.5 million worshippers.[35][36] His successor, King Salman launched five megaprojects as part of the overall King Abdullah Expansion Project in July 2015, covering an area of 456,000 m2 (4,910,000 sq ft). The project was carried out by the Saudi Binladin Group. In 2012, the Abraj Al Bait complex was completed along with the 601 meter tall Makkah Royal Clock Tower.
On 11 September 2015, at least 111 people died and 394 were injured when a crane collapsed onto the mosque. Construction work was suspended after the incident, and remained on hold due to financial issues during the 2010s oil glut. Development was eventually restarted two years later in September 2017.
On 5 March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the mosque began to be closed at night and the Umrah pilgrimage was suspended to limit attendance. The resumption of Umrah service began on 4 October 2020 with the first phase of a gradual resumption that was limited to Saudi citizens and expatriates from within the Kingdom at a rate of 30 per cent.
As of August 2020, the Great Mosque is the largest mosque and the eighth largest building in the world. It has undergone major renovations and expansions through the years. It has passed through the control of various caliphs, sultans and kings, and is now under the control of the King of Saudi Arabia who is titled the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques.
History
The Great Mosque contends with the Mosque of the Companions in the Eritrean city of Massawa and Quba Mosque in Medina as the oldest mosque. Some scholars, who reference Islamic tradition and the Quran, explain that the Islamic perspective claims that Islam as a religion preceded Muhammad, representing previous prophets such as Abraham. Abraham is credited by Muslims with having built the Kaaba in Mecca, and consequently its sanctuary, which according to the Muslim view is seen as the first mosque that ever existed. According to other scholars, Islam started during the lifetime of Muhammad in the 7th century CE, and so did architectural components such as the mosque. In that case, either the Mosque of the Companions or Quba Mosque would be the first mosque that was built in the history of Islam.
Era of Prophet Abraham PBUH and Prophet Ishmael PBUH
According to Islamic doctrine in the Quran, Prophet Abraham PBUH together with his son Prophet Ishmael PBUH raised the foundations of a house, which has been identified as the Kaaba. God showed Prophet Abraham PBUH the exact site which was previously built by Adam PBUH, very near to what is now the ZAMZAM Well, where Abraham and Ishmael began work on the construction of the Kaaba. After Abraham had built the Kaaba, an angel brought to him the Black Stone, a celestial stone that, according to tradition, had fallen from Heaven on the nearby hill Abu Qubays. The Black Stone is believed by Islamic scholars to be the only remnant of the original structure made by Abraham.
After placing the Black Stone in the Eastern corner of the Kaaba, Abraham received a revelation, in which God told the aged prophet that he should now go and proclaim the pilgrimage to mankind, so that men may come both from Arabia and from lands far away, on camel and on foot.
Era of Prophet Muhammad PBUH
Upon Muhammad's victorious return to Mecca in 630 CE, he broke the idols in and around the Kaaba, similar to what, according to the Quran, Abraham did in his homeland.[citation needed] Thus ended polytheistic use of the Kaaba, and began monotheistic rule over it and its sanctuary.
Umayyad era
The first major renovation to the mosque took place in 692 on the orders of Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. Before this renovation, which included the mosque's outer walls being raised and decoration added to the ceiling, the mosque was a small open area with the Kaaba at the center. By the end of the 8th century, the mosque's old wooden columns had been replaced with marble columns and the wings of the prayer hall had been extended on both sides along with the addition of a minaret on the orders of Al-Walid I. The spread of Islam in the Middle East and the influx of pilgrims required an almost complete rebuilding of the site which included adding more marble and three more minarets.
Ottoman era
In 1570, Sultan Selim II commissioned the chief architect Mimar Sinan to renovate the mosque. This renovation resulted in the replacement of the flat roof with domes decorated with calligraphy internally, and the placement of new support columns which are acknowledged as the earliest architectural features of the present mosque. These features are the oldest surviving parts of the building.
 The Great Mosque in an illustration of the Futuh al-Haramayn of Muhi Al-Din Lari, 1582
The Great Mosque in an illustration of the Futuh al-Haramayn of Muhi Al-Din Lari, 1582
 The mosque in 1850, during the Ottoman period
The mosque in 1850, during the Ottoman period
 The mosque in 1910, during the Ottoman period
The mosque in 1910, during the Ottoman period
During heavy rains and flash floods in 1621 and 1629, the walls of the Kaaba and the mosque suffered extensive damage. In 1629, during the reign of Sultan Murad IV, the mosque was renovated. In the renovation of the mosque, a new stone arcade was added, three more minarets (bringing the total to seven) were built, and the marble flooring was retiled. This was the unaltered state of the mosque for nearly three centuries.
Saudi era
First Saudi expansion
The first major renovation under the Saudi kings was done between 1955 and 1973. In this renovation, four more minarets were added, the ceiling was refurnished, and the floor was replaced with artificial stone and marble. The Mas'a gallery (As-Safa and Al-Marwah) is included in the Mosque, via roofing and enclosures. During this renovation many of the historical features built by the Ottomans, particularly the support columns, were demolished.
On 20 November 1979, the Great Mosque was seized by extremist insurgents who called for the overthrow of the Saudi dynasty. They took hostages and in the ensuing siege hundreds were killed. These events came as a shock to the Islamic world, as violence is strictly forbidden within the mosque.
Second Saudi expansion
The second Saudi renovations under King Fahd, added a new wing and an outdoor prayer area to the mosque. The new wing, which is also for prayers, is reached through the King Fahd Gate. This extension was performed between 1982 and 1988.
1988 to 2005 saw the building of more minarets, the erecting of a King's residence overlooking the mosque and more prayer area in and around the mosque itself. These developments took place simultaneously with those in Arafat, Mina and Muzdalifah. This extension also added 18 more gates, three domes corresponding in position to each gate and the installation of nearly 500 marble columns. Other modern developments added heated floors, air conditioning, escalators and a drainage system.
Third Saudi expansion
In 2008, the Saudi government under King Abdullah Ibn Abdulaziz announced an expansion of the mosque, involving the expropriation of land to the north and northwest of the mosque covering 300,000 m2 (3,200,000 sq ft). At that time, the mosque covered an area of 356,800 m2 (3,841,000 sq ft) including indoor and outdoor praying spaces. 40 billion riyals (US$10.6 billion) was allocated for the expansion project.
In August 2011, the government under King Abdullah announced further details of the expansion. It would cover an area of 400,000 m2 (4,300,000 sq ft) and accommodate 1.2 million worshippers, including a multi-level extension on the north side of the complex, new stairways and tunnels, a gate named after King Abdullah, and two minarets, bringing the total number of minarets to eleven. The circumambulation areas (Mataf) around the Kaaba would be expanded and all closed spaces receive air conditioning. After completion, it would raise the mosque's capacity from 770,000 to over 2.5 million worshippers.[35][36] His successor, King Salman launched five megaprojects as part of the overall King Abdullah Expansion Project in July 2015, covering an area of 456,000 m2 (4,910,000 sq ft). The project was carried out by the Saudi Binladin Group. In 2012, the Abraj Al Bait complex was completed along with the 601 meter tall Makkah Royal Clock Tower.
On 11 September 2015, at least 111 people died and 394 were injured when a crane collapsed onto the mosque. Construction work was suspended after the incident, and remained on hold due to financial issues during the 2010s oil glut. Development was eventually restarted two years later in September 2017.
On 5 March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the mosque began to be closed at night and the Umrah pilgrimage was suspended to limit attendance. The resumption of Umrah service began on 4 October 2020 with the first phase of a gradual resumption that was limited to Saudi citizens and expatriates from within the Kingdom at a rate of 30 per cent.
See Also: Coronavirus | Education | Hajj | Health | Islamic Culture And Civilization | Jerusalem | Knowledge | Love | Madinah (Medina) | Makkah (Mecca) | Masjid Al Aqsa | Masjid Al Nabawi | Nature And Environment | Prayers (Salah) | Prophet Muhammad (S) | Ramadan | Spirituality | Taraweeh Prayers | Witr
MOST RECENT
- Sort By
- Views
- Comments
- Duration
Covered Topics- All
- Eid Al-Fitr
- Khatam Quran Dua
- Makkah (Mecca)
- Masjid Al Haram
- Ramadan
- Takbeer
- Taraweeh Prayers